
Plasma Cell Medical laboratory, Hematology, Medical laboratory scientist
Definition Solitary lesions of clonal plasma cells that are cytologically, immunophenotypically, and genetically similar to plasma cell myeloma. Clinical Features Bone pain and cord compression due to vertebral lesions. Localization Dura-based (D.D. meningioma), intrasellar (D.D. pituitary adenoma), rarely intraparenchymal.

Free download Sphere Kanji Clock, Chromatin, purple, violet png PNGEgg
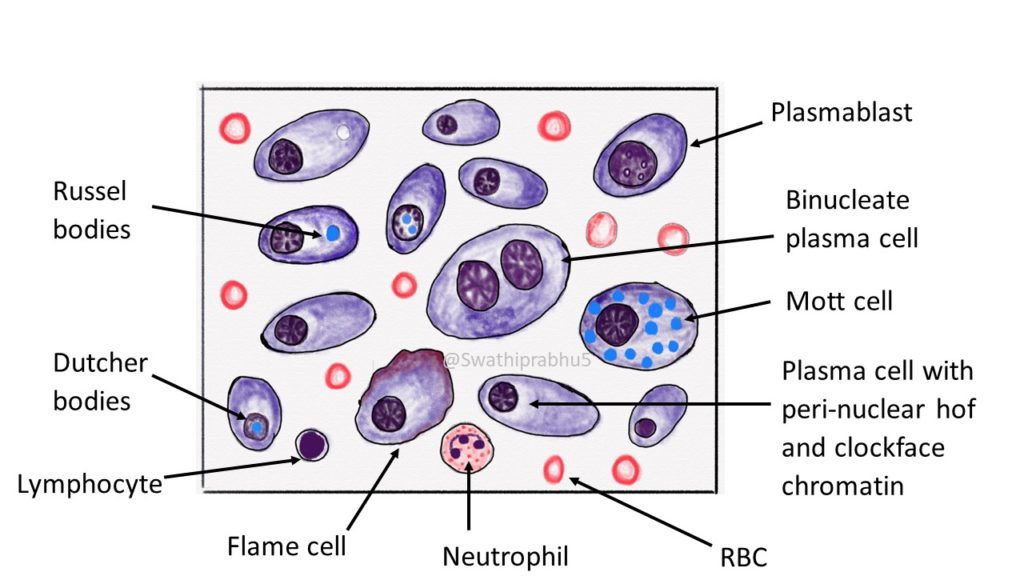
Plasma cells with prominent clock face chromatin Russell bodies Scattered immature plasma cells Scattered Mott cells with grape-like inclusions Board review style answer #3. D. Scattered immature plasma cells are more specific to a neoplastic process compared to binucleation, Russell bodies or mild plasmacytosis.

Plasmablastic lymphoma cells with a plasmacytoid appearence with a
Histochemistry and Cytochemistry Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP RISH V. Application to monoclonal antibody production. Immunodeficiency. Immunodeficiency. Histology, B Cell Lymphocyte. Mechanisms that determine plasma cell lifespan and the duration of humoral immunity.

The basic chromatin structural unit of the plasma cell nucleus (the
Clockface chromatin Plasma cells have distinctive features that are clearly seen in this electron micrograph: a prominent Golgi; well developed rough endoplasmic reticulum; and a nucleus with large clumps of heterochromatin at the margin of the nucleus (clock-face nucleus).. (clock-face nucleus). Compare these features with the high.

JIM.fr De l’importance de la maladie résiduelle négative dans le myélome
Circadian clock and chromatin-remodeling complexes are tightly intertwined systems that regulate rhythmic gene expression. The circadian clock promotes rhythmic expression, timely recruitment, and/or activation of chromatin remodelers, while chromatin remodelers regulate accessibility of clock transcription factors to the DNA to influence expression of clock genes.
(A and B) section shows diffuse plasma cell proliferation composed of
Abstract. Chromatin organization plays a crucial role in gene regulation by controlling the accessibility of DNA to transcription machinery. While significant progress has been made in understanding the regulatory role of clock proteins in circadian rhythms, how chromatin organization affects circadian rhythms remains poorly understood.

Chromatin Structure and Function as a Biological Clock during Aging
Introduction Overview neoplastic proliferation of plasma cells within the bone marrow leads to the production of monoclonal immunoglobulin (Ig) mostly IgG (52%) and IgA (21%) results in skeletal destruction Epidemiology Demographics older adults median age is 66 years of age Risk factors monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS)
Activating chromatin marks are associated with core clock genes, CCA1
summary Multiple Myeloma is neoplastic proliferation of plasma cells that commonly results in multiple skeletal lesions, hypercalcemia, renal insufficiency, and anemia. Patients typically present at ages > 40 with localized bone pain or a pathologic fracture. Diagnosis is made with a bone marrow biopsy showing monoclonal plasma cells ≥10%.

Moran CORE Cellular Histopathology
Pathophysiology refers to changes in bodily processes that result from disease. In the case of multiple myeloma (MM), which is a type of bone marrow cancer, the pathophysiology is complex. It can.
Pathology of Multiple Myeloma Pathology Made Simple
"Clock-face" chromatin pattern. Small dots symmetrically rim the nuclear membrane - like the numbers on a clock. Abundant cytoplasm. Nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio ~1:2 Perinuclear hof (prominent Gogli apparatus). Pale perinuclear crescentic - may be up to the size of the nucleus in active plasma cells. Note:

Multiple Myeloma and Plasma Cell Dyscrasias Oncohema Key
Definition / general. Usually less than 1% of marrow cells; rare in infants. Often perivascular and in particle crush specimens. Indeterminate lifespan ranging from days to months. Produces and secretes antibodies. Plasmablast: precursor to plasma cell, produces more antibodies than B cells but less than mature plasma cells.
Pathological study revealing proliferation of plasmacytoid cells with
Chromatin is heavily clumped, and dense masses of chromatin show the typical "spoke wheel" or "clock face" chromatin pattern. Nucleolus is not visible. The cytoplasm is abundant, always basophilic and usually deep blue. A well-defined large and colorless perinuclear hof is present in almost all PC and corresponds to the uncolored Golgi.

Multiple Myeloma
The plasma cells have eccentric nuclei with characteristic "clock-face" chromatin without nucleoli ( Fig. 9D). 30. Lymphoma. Age and Sex . Primary lymphoma of the sacrum has a peak incidence during the second and third decades of life, affecting more males than females at a ratio of 2:1. 5.

60+ Beautiful Clocks Face That Make The Room Where The Heart Is
Mature plasma cells: oval with abundant basophilic cytoplasm, perinuclear hof, round eccentric nuclei, "clock face" chromatin and indiscernible nucleoli Immature plasma cells: higher nuclear / cytoplasmic ratio, more abundant cytoplasm and hof region compared to plasmablastic, more dispersed chromatin, often prominent nucleoli.

1. Smear showing myeloma cells. [MGG; × 400]. 2. Histopathology section
Another interesting aspect that remains to be fully explored is the evolutionary trajectory of clock and chromatin remodeling. From the initial studies in the model system A. thaliana, research is increasingly advancing in analyses of clock and chromatin function in other non-model plants. The use of multidisciplinary approaches, including.
Plasma cells 1.
. The nucleus and cytoplasm of plasma-cells are enlarged with abundant contents, such as uncompressed chromatin and well-developed endoplasmic reticulum for antibody secretion, respectively. In.